Introduction
Finding what you need would be practically difficult without assistance navigating through the vast quantity of information available on the Internet.
Google’s ranking systems are built to do exactly that: filter through hundreds of billions of sites in our Search index in a fraction of a second to discover the most relevant, helpful results, and present them in a way that makes it easy for you to discover what you’re searching for.
These ranking systems are made up of several algorithms rather than just one. Search engines consider various criteria to provide you with the most relevant information, including the terms in your query, the relevancy and usability of sites, the expertise of sources, and your location and settings.
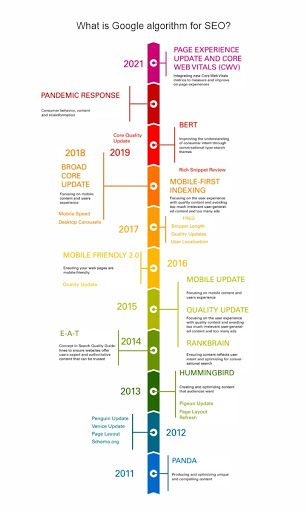
List of Google’s Algorithms & Latest Google Algorithm Updates 2021
Google’s algorithms were only updated a few times in its early years. Every year, Google makes hundreds of updates.
The majority of these changes are so little that they go undetected. On rare occasions, though, the search engine makes large algorithmic changes that have a big influence on the SERPs.
We’ve assembled a comprehensive list of Google algorithm launches, upgrades, and re-launches below.
In recent years, Google’s Search has improved to the point that it can now present suggestions when a user types in a single keyword. This indicates the usage of a new type of algorithm to generate a personalized drop-down menu of search recommendations based on the browser history and other criteria.
So, let us understand how this works!
How Google Algorithm Works?
The keyword search mechanism on Google is comparable to that of other search engines. Spiders or crawlers are automated programs that crawl the Internet, going from link to link and compiling an index page with certain keywords. When a user types in a search query, Google references this index.
The PageRank system, a patented automated mechanism that decides where each search result shows on Google’s search engine return page, is probably the essential aspect of the Google algorithm.
Every search result is given a rank or a score by PageRank. The better the page’s score, the higher it will appear in the search results list.
Some factors that affect the site score are:
- How long the site has been existing
- The strength of the domain name
- How and where the keywords appear on the site
- The age of the links coming to and from the site
Google doesn’t describe in great detail how they function, although it does describe what factors into search results, such as:
- The intent and meaning of a query
- What is the relevance of a certain website to that query?
- The content on mentioned webpage’s quality and dependability
- The web page’s usability
- The context of the person doing the Search, such as their location and past searches
- Purpose and the meaning of a query
Google needs to know what the user is looking for and his search intent to offer relevant results.
They must comprehend and evaluate a variety of issues:
The meaning of the words — what do the words in the natural language mean?
The query’s search intent:
Comprehending intent is a crucial part of Search since it is primarily about understanding language.
Generally, there are four types of search intent: Informational, Navigational, Transactional, and Commercial Investigation. Google identifies the search intent based on certain keywords and thus understands the meaning of a query asked.
- Relevance of the Query
Algorithms now analyze the content of sites to see whether it includes relevant information to what you are looking for.
When a site has the same terms as your search query, this is the most fundamental evidence that the material is relevant. In addition, if certain keywords occur on the website, in the headers, or in the body of the text, the material is more likely to be reliable.
Google employs aggregated and anonymized interaction data in addition to simple keyword matching to determine if search results are relevant to queries. We convert that information into signals that aid our machine-learning systems in determining relevance.
- Webpage Content
Because each search query is likely to result in millions of results, Google must prioritize the ones that provide high-quality material and demonstrate:
- Expertise
- Authority
- Trustworthiness
The so-called PageRank algorithm, which considers the quality and amount of links heading to a website, is one of the most important components.
- Usability of Webpage
When ranking results, Google Search considers how user-friendly a website is. When we find recurring user pain points, we create algorithms that favor more usable sites over less usable pages, all other factors being equal.
These algorithms look for signals that indicate whether all of our users can see the result, such as whether the site looks good in different browsers, whether it’s designed for all device types and sizes, such as desktops, tablets, and smartphones, and whether the page loading times are fast enough for users with slow Internet connections.
- User Context
Last but not least, the user’s circumstances and preferences have a significant impact on the search results. These might include the following:
- The user’s current location
- Searching history
- Options for searching
Your location, previous search history, and Search preferences all aid Google in tailoring your results to what is most useful and relevant for you at the time.
Conclusion
Many of us take it for granted that we can get important information on the Internet. However, there are almost 150,000,000 active Web sites on the Internet today.
Going through all of those websites in Search of useful information is a tremendous undertaking. That’s why search engines employ sophisticated algorithms, which are mathematical instructions.
Also, it is very important that your website rank on the first page of the website to have maximum visibility. Hence, we are here to do the job for you. So, connect to us for more information!

